This post summarizes key ideas in the conference paper “Blockchain for 5G: Opportunities and Challenges”.
5G Primary Features
- User peak data rate of 10 Gbps
- 1 million devices per square kilometer
- 10 Tbps per square kilometer
- 1 millionsecond latency
- Network Function Virtulization (NFV) and Software Defined Networking (SDN)
Opportunities by Blockchain
Financing method, Sharing platform, Marketplace, Validation program
5G Infrastructure Crowdsourcing
Allow smaller infrastructure investors to roll out cellular towers that will be part of the overall operator’s infrastructure.
Tower owners register tower information (e.g., capability, hardware, pricing, availability, attestation, certification, reputation history) to the samrt contract.
Mobile operators select particular towers to lease.
5G Infrastructure Sharing
Active Sharing: Radio Access Network (RAN), Gateway Core Network (GWCN)
Passive Sharing: tower mast, space, cooling, telecom rooms
National Roaming
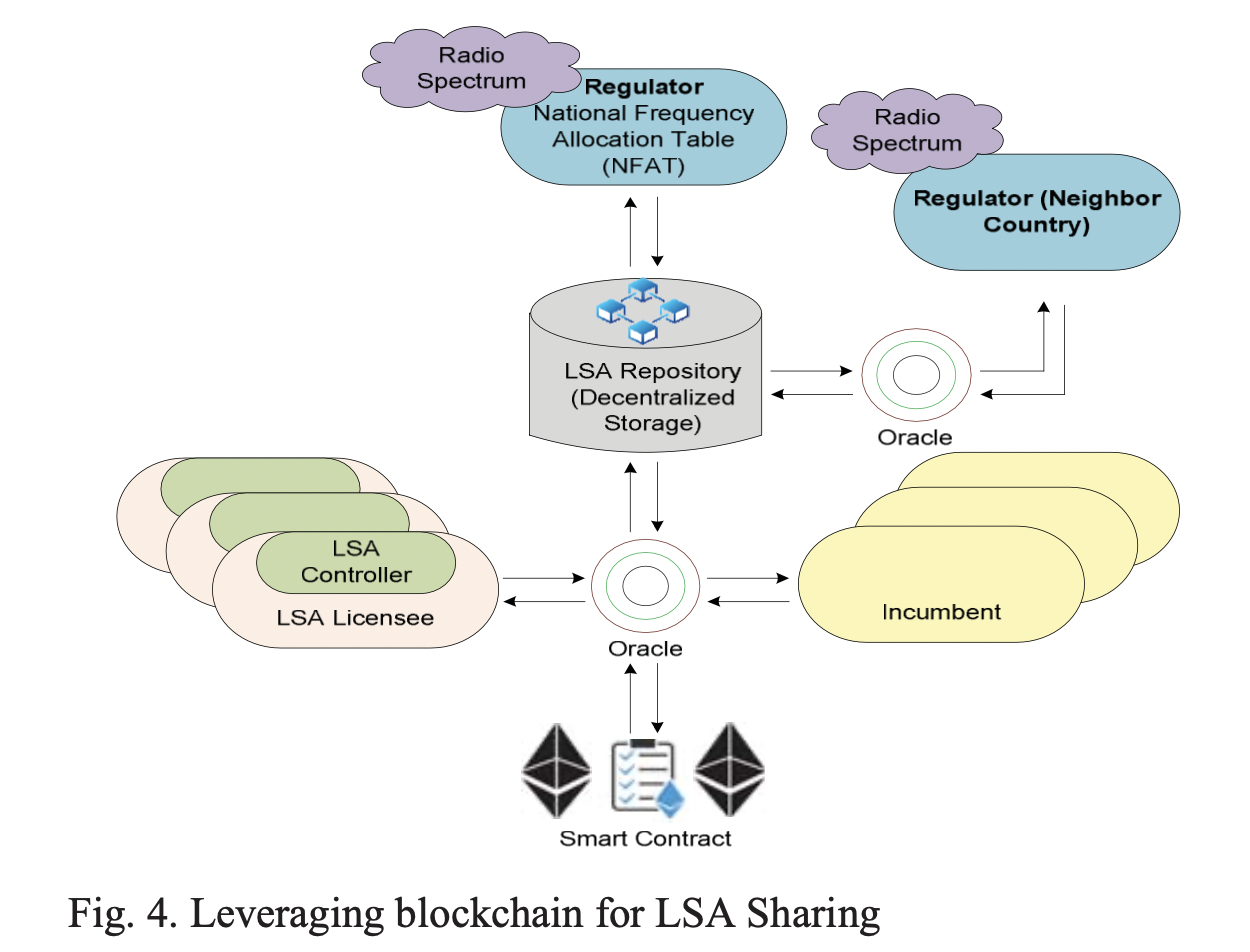
Spectrum Sharing
License Shared Access (LSA) scheme provides a part of unused spectrum to the incumbent user, whereby the LSA licensee is granted for using part of its incumbent spectrum.
International Roaming
Roaming interconnections are settled either by direct or by international exchanges.
The international exchanges have some critical drawbacks, such as
- single point of failure in the intermediary level
- profit-cut (that these intermediaries regularly charge)
- fraudulent activities (that may occur if the roaming subscriber usage is not directly exchanged)
Network Slicing
A Network Slice Broker (NSB) is typically used to perform the slicing by exposing the service capabilities of the mobile operator network. A blockchain smart contract with decentralized storage, like Storj or IPFS can be used to replace some or all NSB functionalities.
Management and Authentication of mMTC and uRLLC
- Massive Machine Communication (mMTC)
- Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communication (uRLLC)
The centralized operator needs to perform following jobs, which can be faciliated by blockchain smart contracts.
- manage subscriptions, payments, and data bundles
- manage multiple verticals and multiple enterprises
- manage device authentication
Challenges
Scalability
Smart Contracts
- How to transform existing smart contracts into smart contracts for 5G ecosystem? (design problem)
- Legality of smart contract deployment.
- Security of smart contract code: bugs and vulnerability.
- How to upgrade or patch published smart contracts?
Standardization and Regulations
Transaction and Cloud Infrastructure Costs
Costs to host blockchain nodes
Data Privacy
No personal data shall be stored in blockchain, only has pointers of that information
Interoperability
New technologies of 5G work in a different fashion:
- mmWave
- Small cells
- mMIMO
- Full duplex
- SDN
- Beamforming
