This is the course project of NTU CE7412: Computational and Systems Biology by Professor Jagath Rajapakse. The full report is here.
Protein function prediction is a key area of research in bioinformatics that involves the use of computational methods to predict the biological functions of proteins. It predicts the key Gene Ontology Terms (function) based on the protein sequence data. It is an important field because understanding the function of proteins is essential for understanding cellular processes and disease mechanisms, as well as for the development of new drugs and therapies.

There are multiple approaches to predict protein functions, such as using sequence-based features, protein-protein interaction networks, protein structures, and biomedical literature. Among them, the protein’s amino acid sequence is the most available information for most of proteins. Therefore, methods that can precisely forecast protein functions solely based on sequence could be the most comprehensive and widely applicable to proteins that lack extensive research. Conventional techniques aim to identify comparable sequences that possess known functional annotations and distinct sequence motifs linked with specific functions.
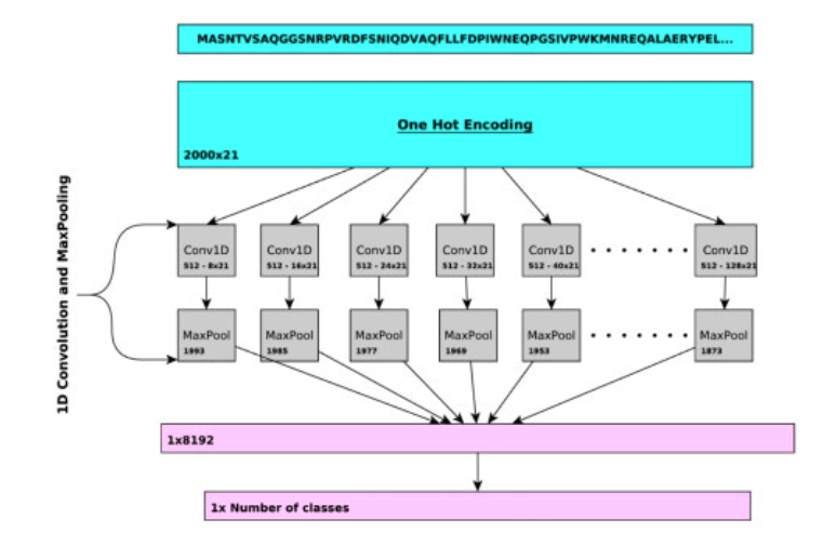
Recent machine learning methods demonstrate more advantages in scalability for handling large-scale problems, automated feature extraction without the need for human knowledge, robustness for noisy data, and adaptability for different datasets. DeepGO is one of the first deep learning models which can predict protein functions using the protein amino acid sequence and interaction networks. However, DeepGO has several restrictions on the sequence length, missing features and number of predicted classes. DeepGOPlus has been proposed to overcome these issues, which is based on Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) using multiple 1D convolution layers. However, based on what has been found in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP), CNNs are not the most effective model handling sequential data. Models like Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), Long-Term-Short-Memory (LSTM), and transformer demonstrate more promising performance than CNNs for sequential data.
Therefore, this project aims to benchmark advanced sequence learning models as mentioned and their hybrid architectures against DeepGOPlus. Performance metrics like F-score, semantic distance, and precision-recall area are compared among various models using CAFA3 and SwissProt datasets. Their advantages and disadvantages are analyzed for RNN, LSTM, Transformer, and hybrid architectures.